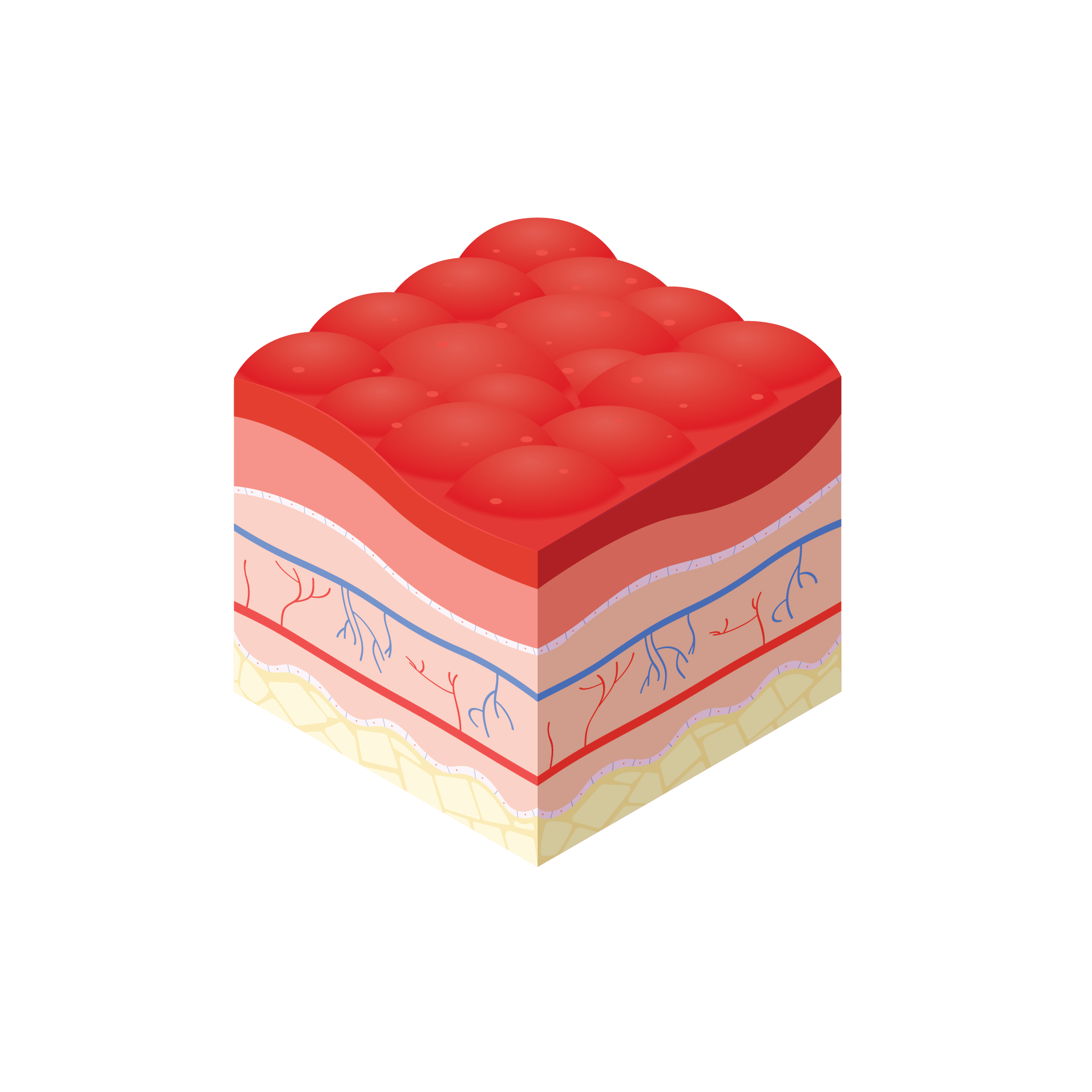
Što je granulirajuća rana
Granulacija opisuje pojavu crvenog, zrnatog tkiva na području rane prilikom cijeljenja. Ova zrnatost predstavlja vidljive vrhove novonastalih kapilarnih spletova, koji imaju ulogu opskrbljivati novonastalo tkivo kisikom i hranjivim tvarima¹.
Promjene u normalnoj granuliranosti, vlažnosti i svijetlocrvenoj boji granulacionog tkiva mogu ukazivati u osnovi na probleme. Ako se granulacijsko tkivo razvije do te mjere da se izdiže iznad okolne kože to se zove hipergranulacija ili prekomjerna granulacija.
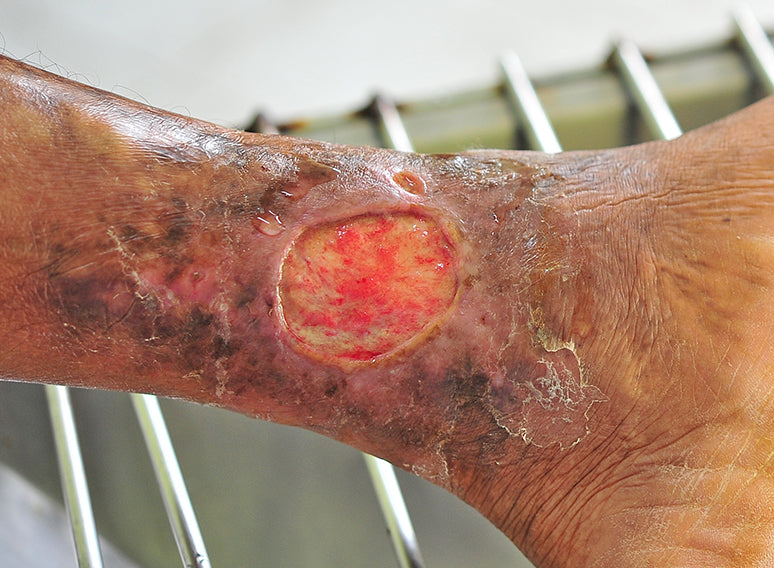
Ciljevi liječenja
Cilj liječenja treba biti poticanje toplih i vlažnih uvjeta na rani kroz uravnoteženu kontrolu eksudacije.
Products that treat Granulating Wounds

Learn More
With the Education HubWant to learn more about a range of different wound types and how they can be treated? Visit our free Education Hub.
Wound Types
Select a wound type below to discover more...
-

Necrotic tissue is dead or devitalised non-viable tissue which impedes wound healing.
-

Slough refers to the yellow/white material in the wound bed.
-

Epithelialisation is the final stage of wound healing and is pink/white in colour.
-

Cavity wounds can be defined as a wound that extends beneath the dermis.
-

A fungating wound develops when cancer that is growing under the skin breaks through the skin and creates a wound.
-

A scar may appear flat, lumpy, sunken, or coloured.
-

Infection can develop in any type of wound and is usually accompanied by pain, inflammation and swelling.
-

Return to the Wound Guide Information Page
References
1. Dealey C (2012) The Care of Wounds. (4th edn). Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester